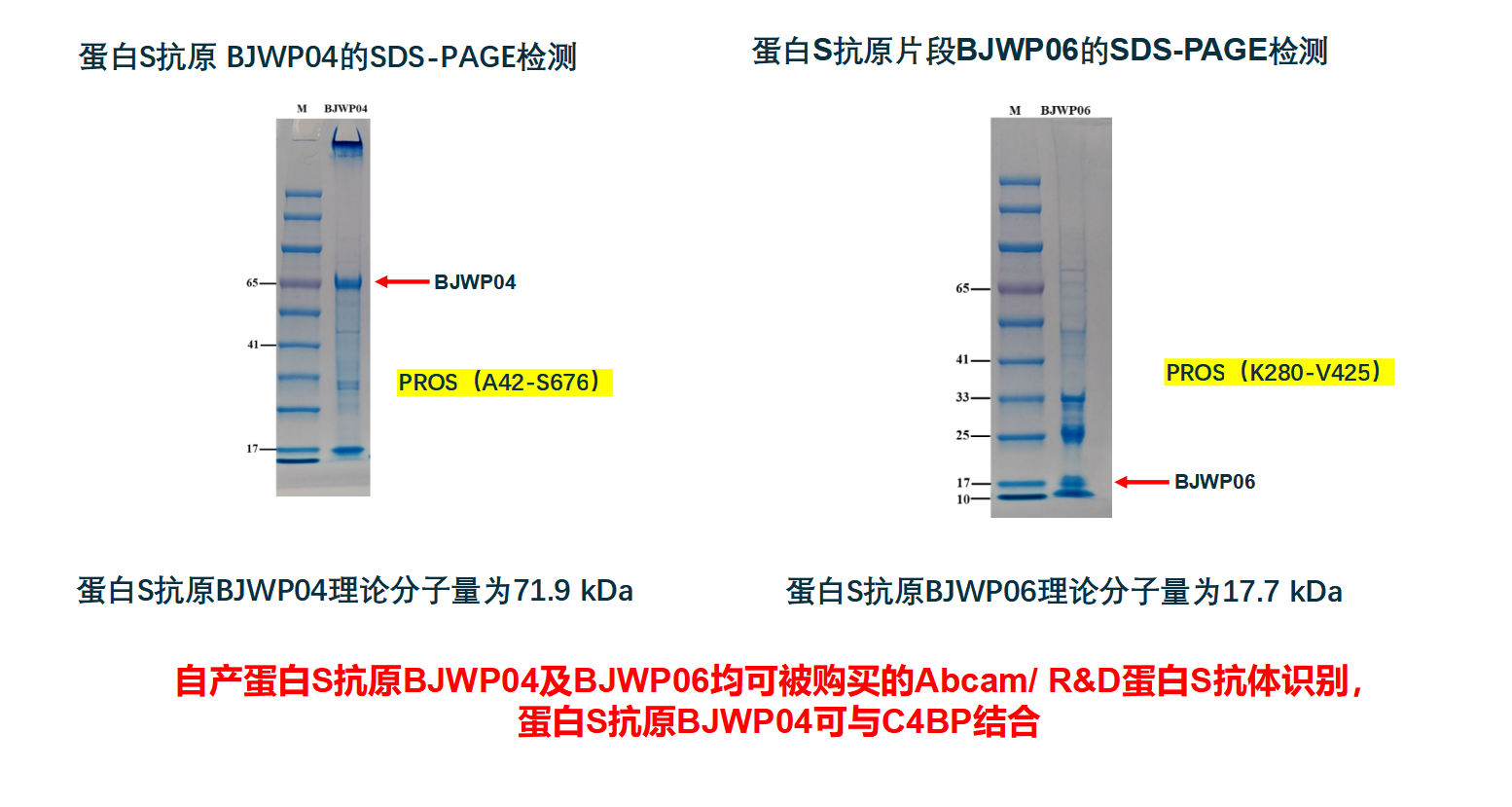
一、产品介绍
蛋白 S 是一种维生素 K 依赖血浆蛋白,是活化蛋白 C(蛋白 Ca ,APC)的辅因子。通过蛋白 Ca 使凝血因子 Va、 Ⅷa 水解失活 。蛋白S 活性降低见于危险性增加。2021年《易栓症诊断与防治中国指南》在易栓症和VTE患者病因筛查中推荐进行蛋白S活性检测。多个省份已将蛋白S检测纳入医保范畴。
BACKGROUND Anticoagulant Protein S (PROS1) is a 71 kDa plasma vitamin K-dependent glycoprotein characterized by the presence of the post-translational modification of specific glutamic acid residues to gamma-carboxyglutamic acid (Gla) in the N-terminal region. In addition to the N-terminal Gla domain, mature PROS1 contains a thrombin?sensitive thumb loop, four tandem EGF-like domains and a C-terminal sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) domain composed of two Laminin G (LG) domains (1). Human PROS1 shares 80% amino acid sequence identity with mouse PROS1. Hundreds of mutations have been reported throughout all the domains of the protein, typically resulting in PROS1 deficiency and an increase in the risk of thrombophilia (2, 3). PROS1 is expressed in many cell types supporting its reported involvement in multiple biological processes that include coagulation, apoptosis, cancer development and progression, and the innate immune response (4-9). PROS1 exists in plasma both in complex with C4b-binding protein (C4BP) (60%) and in a free form (40%). Both forms of PROS1 have anti-coagulant activity either directly through inhibition of Factor X systems and prothrombinase while in complex with C4BP (5, 10) or in its well-established role as a cofactor of activated protein C (APC) inactivation of procoagulants FVa and FVIIIa (4). The free form of PROS1 is also a ligand for a subfamily of receptor tyrosine kinases known as TAMs, which is composed of TYRO3, AXL, and MERTK (11). PROS1 binds these tyrosine kinase receptors through its LG domains to activate downstream signaling pathways involved in tumor development and progression (7, 8, 11, 12)
二、PS类型
PS在血液中有两种形式: 游离型PS(简称FPS),约占40% 结合型PS(与C4b结合蛋白结合),约占60% 其中,仅游离型PS能提升APC的抗凝活性,参与APC对Va和VⅢa的灭活。
三、产品特点